Blockchain technology has evolved into a cornerstone of digital innovation, reshaping industries and driving the future of decentralized systems. While it initially gained prominence as the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, blockchain’s applications now extend far beyond financial transactions. This article explores the essential components, types, real-world applications, challenges, and steps to get started with Understanding blockchain technology, along with the latest trends shaping its future.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized and distributed ledger that records transactions in a secure, transparent, and immutable manner. Each transaction is grouped into blocks, linked chronologically to form a chain. This structure ensures that data is tamper-proof and accessible to all participants in the network.
Key Features of Blockchain
- Decentralization: Eliminates the need for intermediaries by operating on a peer-to-peer network.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be altered without consensus from the network.
- Transparency: All participants have access to the ledger, fostering trust.
- Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques protect data from unauthorized access.
Blockchain’s ability to ensure trust and transparency has made it an essential tool across various industries.
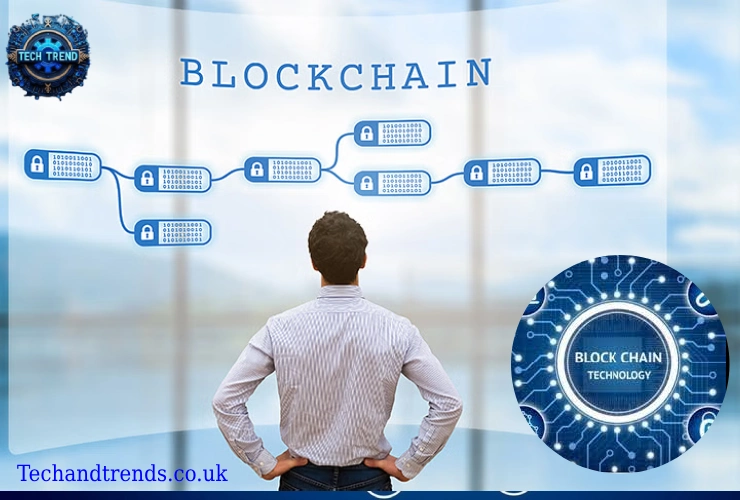
Essential Components of Blockchain
Understanding blockchain technology requires familiarity with its fundamental building blocks:
1. Blocks
Each block contains:
- Header: Metadata such as the timestamp and hash of the previous block.
- Data Section: Transaction details or other relevant information.
- Hash: A unique cryptographic identifier for the block.
2. Nodes
Nodes are individual devices in the blockchain network that maintain copies of the ledger and validate transactions.
3. Consensus Mechanisms
These protocols ensure agreement among nodes on the validity of transactions. Popular mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): Requires solving complex mathematical problems (used by Bitcoin).
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are selected based on their stake in the network.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Enhance privacy by verifying transactions without revealing sensitive data.
| Read More Informative Articles |
|---|
| Fani Willis Net Worth |
| Olivia Culpo Net Worth |
| Natalie Nunn Net Worth |
Different Types of Blockchains
Blockchain technology is not monolithic; it comes in various forms tailored to specific use cases:
- Public Blockchains
- Open to everyone.
- Examples: Bitcoin, Ethereum.
- Use Cases: Cryptocurrencies, decentralized applications (dApps).
- Private Blockchains
- Restricted access; controlled by an organization.
- Examples: Hyperledger Fabric.
- Use Cases: Enterprise solutions like supply chain management.
- Consortium Blockchains
- Governed by multiple organizations.
- Example: R3 Corda.
- Use Cases: Banking collaborations and shared databases.
- Hybrid Blockchains
- Combine public and private blockchain features.
- Use Cases: Real estate transactions and healthcare data sharing.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain’s versatility has led to its adoption across numerous sectors:
1. Finance
- Enables faster cross-border payments with reduced fees (e.g., Ripple).
- Powers decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms offering loans, insurance, and investments without intermediaries.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Tracks goods from origin to destination for enhanced transparency and fraud prevention (e.g., IBM Food Trust).
3. Healthcare
- Secures patient records while enabling seamless data sharing among authorized parties.
4. Real Estate
- Simplifies property transactions by eliminating intermediaries and ensuring transparent ownership records.
5. Gaming and Entertainment
- Powers non-fungible tokens (NFTs) for digital ownership of art, music, and collectibles.
6. Government Services
- Enhances voting systems with tamper-proof digital ballots.
Latest Innovations in Blockchain Technology
As we move into 2025, blockchain technology continues to evolve with groundbreaking advancements:
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Governments worldwide are adopting CBDCs for secure digital payments, reducing reliance on cash while enhancing financial inclusivity. - Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Technologies like Zero-Knowledge Rollups (ZK-Rollups) are improving Ethereum’s scalability by reducing gas fees and increasing transaction speeds. - Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Combining blockchain with AI enables intelligent systems capable of analyzing large datasets while maintaining security and transparency. - Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Companies like Microsoft and Amazon offer BaaS platforms that allow businesses to build blockchain-based applications without extensive infrastructure investments. - Green Blockchain Initiatives
Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof of Stake are helping blockchains align with global climate goals by reducing carbon footprints. - Decentralized Social Networks
Blockchain-based social platforms ensure user privacy and content authenticity, addressing concerns over data misuse by centralized tech giants.
Challenges and Key Considerations
Despite its potential, understanding blockchain technology also involves acknowledging its challenges:
- Scalability Issues
High transaction volumes can overwhelm networks like Ethereum, causing delays and increased costs. - Energy Consumption
PoW-based blockchains consume significant energy due to mining activities, though newer mechanisms aim to address this issue. - Regulatory Uncertainty
Governments worldwide are still formulating policies for blockchain-based systems, creating uncertainty for businesses and developers. - Interoperability
The lack of standardization makes it difficult for different blockchains to communicate effectively. - Skill Gap
The demand for blockchain experts far exceeds the supply, posing challenges for widespread adoption.
How to Get Started with Blockchain
If you’re intrigued by blockchain’s potential, here are steps to begin your journey:
- Learn the Basics
Understand key concepts like decentralization, cryptography, and consensus mechanisms through online resources or courses. - Explore Blockchain Platforms
Experiment with platforms like Ethereum or Hyperledger to gain hands-on experience in building dApps or smart contracts. - Develop Smart Contracts
Learn programming languages like Solidity for Ethereum or Rust for Solana to create self-executing contracts. - Join Communities
Engage with blockchain forums or attend meetups to stay updated on trends and developments in the industry. - Earn Certifications
Obtain credentials from recognized institutions like Coursera or Simplilearn to validate your expertise in blockchain technology.
Final Thoughts on Blockchain
Understanding blockchain technology reveals its transformative potential across industries—from enhancing transparency in supply chains to revolutionizing financial systems through DeFi platforms. With advancements in consensus mechanisms, integration with AI, and regulatory clarity on the horizon, blockchain is cementing its role as a foundational pillar of Web3 innovation.
However, challenges such as scalability issues and regulatory concerns must be addressed for widespread adoption. By staying informed about emerging trends like CBDCs, green initiatives, and decentralized social networks, individuals and organizations can harness blockchain’s power to drive innovation in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, one thing is clear—blockchain technology is no longer just an experimental concept; it is a transformative force shaping the future of how we interact with data, trust systems, and each other in an increasingly interconnected world.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology is transforming industries with its decentralized and transparent nature. It enhances security, reduces fraud, and increases efficiency in various sectors, including finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. As organizations adopt this technology, they experience improved data integrity and streamlined operations, making blockchain an essential part of the digital future.
Despite its benefits, blockchain also presents challenges, such as scalability issues, regulatory concerns, and high energy consumption. However, continuous innovation and development are addressing these hurdles. Understanding Blockchain Technology is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to leverage its potential. By learning and adapting, they can take advantage of this revolutionary technology and stay ahead in the evolving digital landscape.
Comments are closed.